Carbon sinks, carbon quotas, carbon trading, CCUS、CCER、 Carbon Knowledge Encyclopedia
Release time:2021-06-23 Views:3613
Editor's note: According to the national unified deployment, the national carbon market will launch online trading before the end of June this year! But what exactly is carbon trading? I'm afraid many people may not be able to explain it clearly. Today, I will mainly review the terminology and concepts behind carbon neutrality, carbon trading, and carbon quotas, hoping to be helpful to everyone.
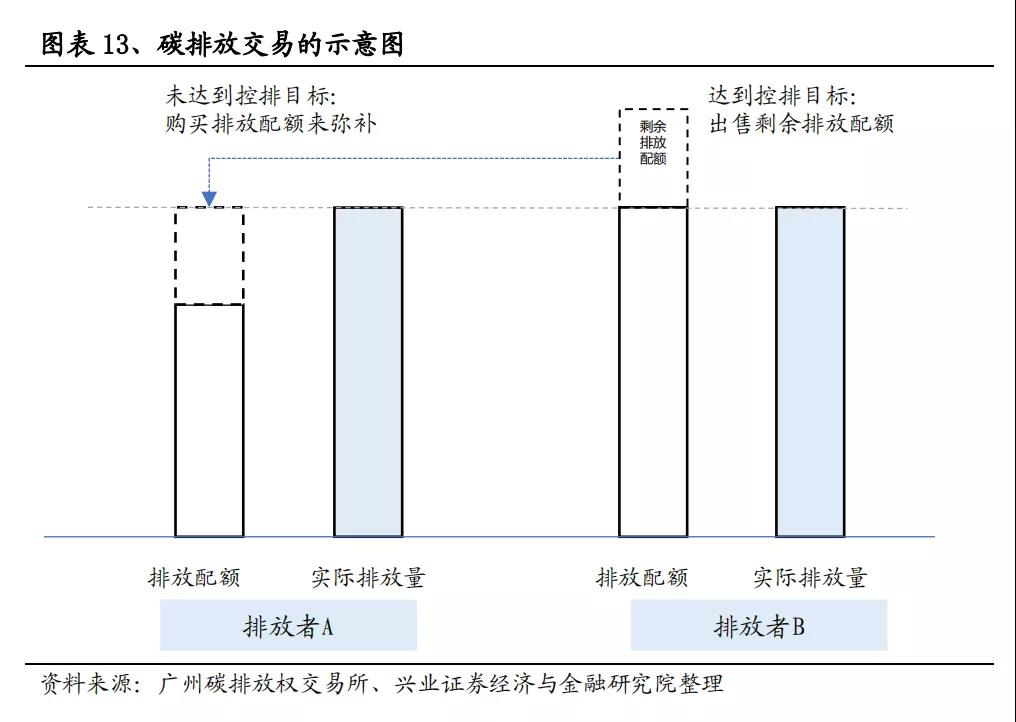
The process of implementing carbon trading can be described as follows with a simple example:
1) At the beginning of the year, there were two companies, A and B. Company A was required to emit 100 tons of carbon dioxide per year, while Company B was also required to emit 100 tons of carbon dioxide per year; The carbon quota issued by the government to A is 100 tons per year, and the carbon quota issued to B is also 100 tons per year;
2) At the end of the year, Company A achieved energy-saving transformation and only emitted 80 tons of carbon dioxide. The excess 20 tons of carbon dioxide quota can be sold on the carbon trading market for profit.
On the other hand, Company B may have worked overtime to expand production capacity, without the time and funds to carry out energy-saving renovations, resulting in carbon dioxide emissions reaching 120 tons, which is 20 tons more than the 100 ton carbon quota given by the government. At this time, Company B can only purchase 20 tons of carbon quotas on the carbon trading market.
In this way, the remaining carbon quotas of Company A have met the carbon emission needs of Company B, and carbon trading has finally been realized. The ultimate effect is that the total carbon dioxide emissions of A and B are locked at 200 tons, without exceeding the initial quota limit of 200 tons, achieving the carbon reduction target.
1、 What is carbon emissions?
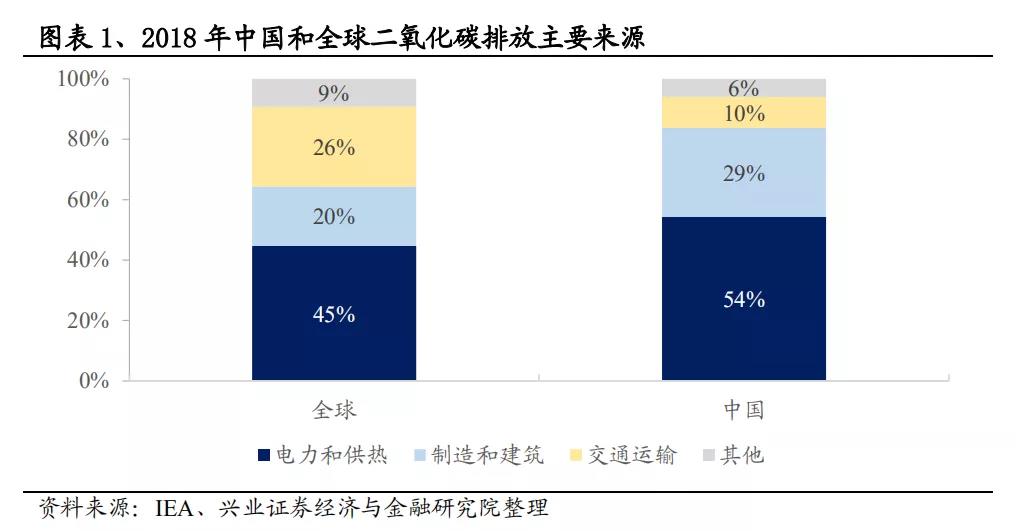
Carbon emissions refer to the process of emitting greenhouse gases (such as carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons, and sulfur hexafluoride) to the outside world during human production and business activities. Carbon emissions are currently considered one of the main causes of global warming. The largest proportion of carbon emissions in China (54%) comes from the combustion of fossil fuels in the production process of the power and heating sectors.
2、 What is carbon peaking?
Broadly speaking, carbon peak refers to a point in time when carbon dioxide emissions no longer increase and reach their peak, and then gradually decline. According to the World Resources Institute, carbon peaking is a process in which carbon emissions first enter a plateau period and can fluctuate within a certain range, and then enter a stable decline stage.
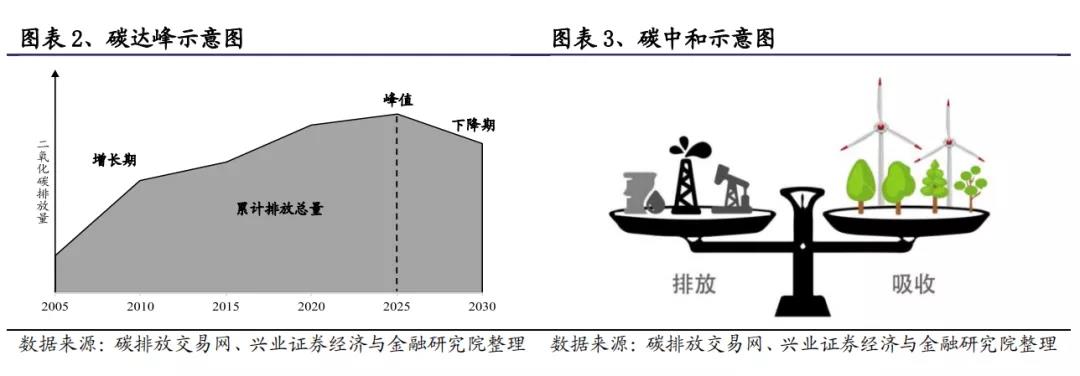
Peak carbon emissions are a prerequisite for achieving carbon neutrality, and achieving peak carbon emissions as early as possible can promote the early realization of carbon neutrality. Based on this, combined with the timeline of China's commitments: 1) From now until 2030, China's carbon emissions will still be in a climbing period; 2) Between 2030 and 2060, carbon emissions will have to cross the plateau period and ultimately complete the emission reduction task.
3、 What is carbon neutrality?
Carbon neutrality refers to the calculation of the total amount of greenhouse gas emissions directly or indirectly generated by enterprises, groups, or individuals over a certain period of time, and then offsetting their own carbon dioxide emissions through afforestation, energy conservation, and emission reduction, achieving "zero carbon dioxide emissions".
4、 What is Carbon Sink?
Carbon Sink: Generally refers to the process, activity, and mechanism of removing carbon dioxide from the air. It mainly refers to the amount of carbon dioxide absorbed and stored by forests, or in other words, the ability of forests to absorb and store carbon dioxide.
Research data shows that China's carbon sequestration capacity is gradually improving. Through vigorous cultivation and protection of artificial forests, China's terrestrial ecosystems absorbed an average of about 1.11 billion tons of carbon per year from 2010 to 2016, accounting for 45% of anthropogenic carbon emissions during the same period. This indicates that forestry carbon sequestration plays an important role in the vision of carbon neutrality, and carbon sequestration projects will help China achieve its carbon neutrality goals.
5、 What is Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS)?
Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS), abbreviated as CCUS, is a technology that captures and purifies the carbon dioxide emitted during the production process, and then inputs it into new production processes for recycling or storage. Among them, carbon capture refers to the collection of carbon dioxide emitted from large power plants, steel plants, cement plants and other emission sources, and its storage in various methods to avoid its emission into the atmosphere.
This technology has the synergistic effect of achieving large-scale greenhouse gas emissions reduction and low-carbon utilization of fossil fuels, and is one of the important technological choices for the future global response to climate change.
6、 What is Carbon Emission Right (CER)?
The origin of carbon emission rights, also known as Certification Emission Reduction (CER). In 2005, with the entry into force of the Kyoto Protocol, carbon emission rights became an international commodity. The subject of carbon emissions trading is called "Certified Emission Reductions (CERs)".
Where do emission rights come from? The primary and secondary markets coexist with quotas.
1) The primary market is generally a market where quotas are initially issued by the development and reform commissions of each province, and is divided into free distribution and paid distribution.
Among them, paid allocation is accompanied by a bidding mechanism, following the principle of quota compensation and equal rights and prices, and conducted in a closed bidding manner.
2) The secondary market is a market where controlled emission enterprises or investment institutions conduct transactions.
7、 What is carbon trading?
Carbon trading refers to the trading of carbon dioxide emission rights as a commodity, in which the buyer obtains a certain amount of carbon dioxide emission rights by paying a certain amount to the seller, thus forming the transaction of carbon dioxide emission rights.
The carbon trading market is a market artificially created by the government through controlling emissions from energy consuming enterprises. Usually, the government determines a total carbon emission amount and allocates carbon emission quotas to enterprises according to certain rules. If the future emissions of enterprises exceed the quota, they need to purchase quotas from the market. At the same time, some enterprises can sell their excess quotas through the carbon trading market if their carbon emissions are lower than the quotas they obtain by adopting energy-saving and emission reduction technologies. Both parties usually trade through carbon emission exchanges.

In the first scenario, if the cost of reducing emissions for a company is lower than the carbon trading market price, the company will choose to reduce emissions, and the share generated from emissions reduction can be sold for profit;
In the second scenario, when the cost of emission reduction for enterprises is higher than the carbon market price, they will choose to purchase from the government, enterprises, or other market entities that have quotas in the carbon market to achieve the emission reduction targets set by the government. If the quota is not purchased in full to cover its actual emissions, it will face high fines.
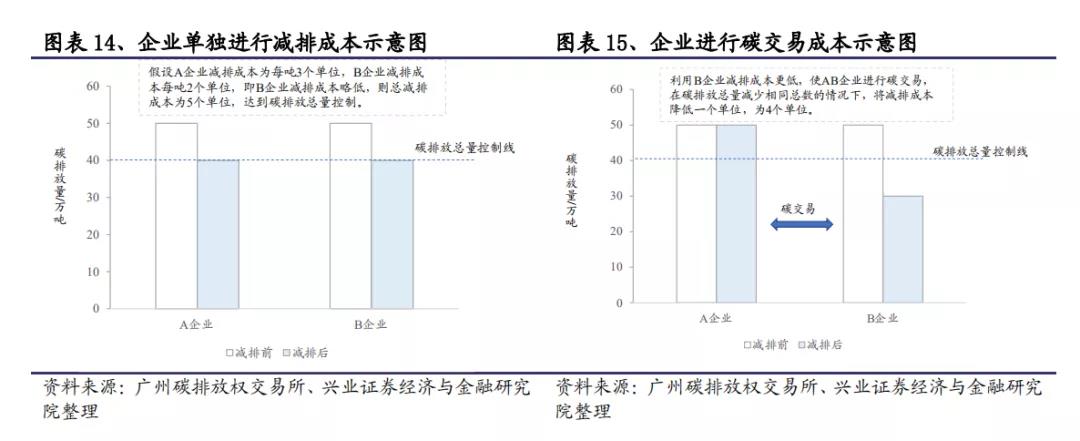
Through this design, the carbon trading market internalizes carbon emissions as part of the operating costs of enterprises, and the carbon emission prices formed by trading guide enterprises to choose the most cost-effective carbon reduction methods, including energy-saving and emission reduction transformation, carbon quota purchase, or carbon capture. The market-oriented approach ensures that while the industrial structure transitions from high energy consumption to low energy consumption, the overall cost of emission reduction in society remains optimal.
8、 What are carbon emission quotas and voluntary emission reductions (CCER)?
According to the classification of carbon trading, there are currently two types of basic products in China's carbon trading market: one is the carbon emission quota allocated by the government to enterprises, and the other is the Certified Voluntary Emission Reduction (CCER).
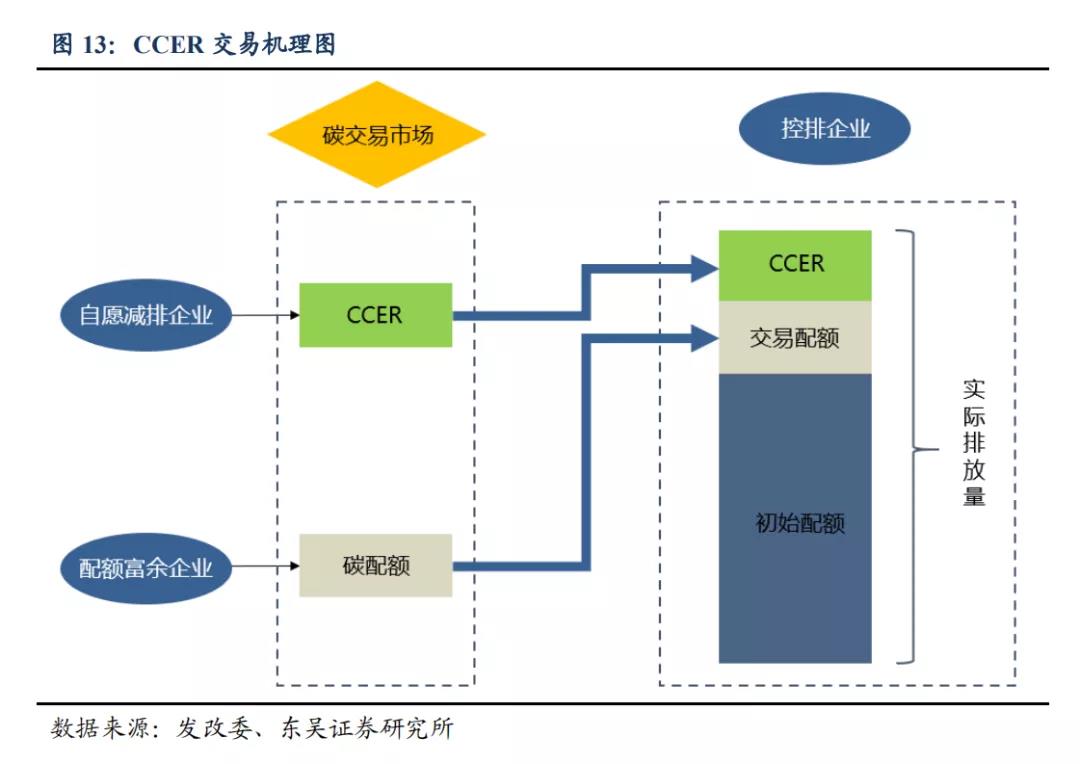
The "Management Measures for Carbon Emission Trading (Trial)" released in December 2020 states that CCER refers to the quantitative verification of the greenhouse gas emission reduction effects of renewable energy, forestry carbon sinks, methane utilization and other projects within China, and the registration of greenhouse gas emission reductions in the national voluntary greenhouse gas emission reduction trading registration system.
The first type is quota trading, which is a policy tool adopted by the government to achieve emission control targets. Within a certain space and time, the emission control targets are converted into carbon emission quotas and allocated to lower level governments and enterprises. If the actual carbon emissions of the enterprise are less than the quota allocated by the government, the enterprise can trade the excess carbon quotas to achieve the reasonable allocation of carbon quotas among different enterprises, and ultimately achieve the emission control targets at a relatively low cost.
The second type, as a supplement, introduces voluntary emission reduction market trading outside the quota market, namely CCER trading. The CCER transaction accuses emission companies of purchasing certified amounts that can be used to offset their own carbon emissions from companies implementing "carbon offsetting" activities.
Carbon offset "refers to the activity of reducing greenhouse gas emission sources or increasing greenhouse gas absorption sinks to compensate for or offset greenhouse gas emissions from other emission sources. That is, the carbon emissions of controlled emission enterprises can be offset by non controlled emission enterprises using clean energy to reduce greenhouse gas emissions or increase carbon sinks. Offset credits are issued after obtaining emission reductions through the implementation of specific emission reduction projects, including renewable energy projects, forest carbon sink projects, etc.
The carbon market provides CCER as a substitute for carbon emission quotas in a 1:1 ratio, meaning that one CCER is equivalent to one quota, which can offset one ton of carbon dioxide equivalent emissions. The "Management Measures for Carbon Emission Trading (Trial)" stipulate that key emission units can use nationally verified voluntary emission reductions to offset the payment of carbon emission quotas each year, and the offset ratio shall not exceed 5% of the carbon emission quotas that should be paid.
Source: New Infrastructure Construction
Disclaimer | Our company maintains neutrality regarding reprints, sharing, statements, and viewpoints, with the sole purpose of communicating with the industry. Copyright belongs to the original author. If there are any copyright or intellectual property infringement issues, please contact our company and delete the content immediately!